Hailstorms in some areas are a common occurrence yet making decisions on what to do with a damaged crop can be agonizing. The following guidelines can be utilized to assess losses.
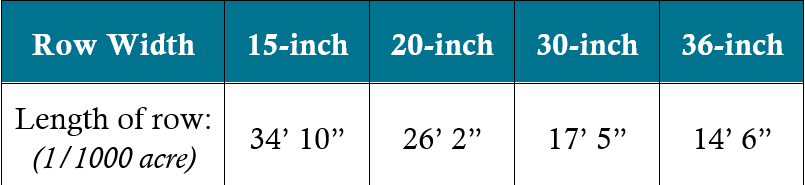
A convenient way to assess a crop stand after a storm is by counting the plants in 1/1,000 of an acre, then multiplying all counts by 1,000. Check several areas of a field, as hail damage can vary greatly throughout a field.
Table 1: Row lengths equal to 1/1000th of an acre.
Prior to the corn reaching a height of 8 inches, the growing point remains protected below the ground surface and stand losses are less likely. However, with severe hail, plants can be damaged to the point that death is a result. If time permits, observations should be made 7-10 days following the damage for accurate conclusions.
If the growing point is present above ground you should always check for damage. Healthy growing points are white and firm. Injured growing points are soft and in time, will begin to turn brown similar to frost damaged plants. If observations are made immediately following a hailstorm, damaged plants can be overlooked. Be conscious of bruises on the stalks of small plants.
Estimating yield reductions due to stand reduction through the 10th actual leaf stage can be calculated utilizing Table 2. When considering a replant situation it is also important to consider planting dates as they relate to potential yields. For example, it may be beneficial to leave a stand reduced to 20,000 plants per acre vs. replanting on June 1 to establish a stand of 32,000 plants per acre. Utilize Table 3 for percentage of expected yield. Other factors to consider when utilizing Table 2 and Table 3 include:
- Gaps and skips have a negative effect.
- Both tables relate to stand reductions during the vegetative stages.
- Consider the hybrid's ability to flex ear size, or yield at low populations.
- Weed control can negatively affect final yields.
Table 2: Estimated percent corn yield loss due to stand reduction occurring through the 10th-leaf growth stage.
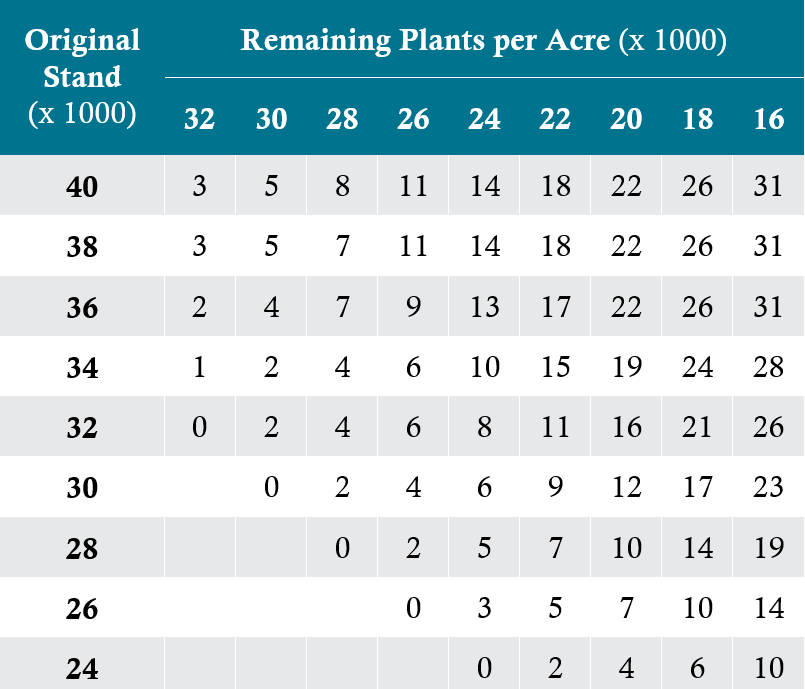
Source: Corn Loss Adjustment Standards Handbook FCIE-2508 (11-2009) 2010 and Succeeding Crop Years.
For more information concerning replant dates and expected yields, refer to the Crop Insights publication, “Hybrid Maturity Switches Based on Long-term Research,” available online in the Agronomy Library at Pioneer.com.
Table 3: Yield potential for a range of plant populations and planting dates.
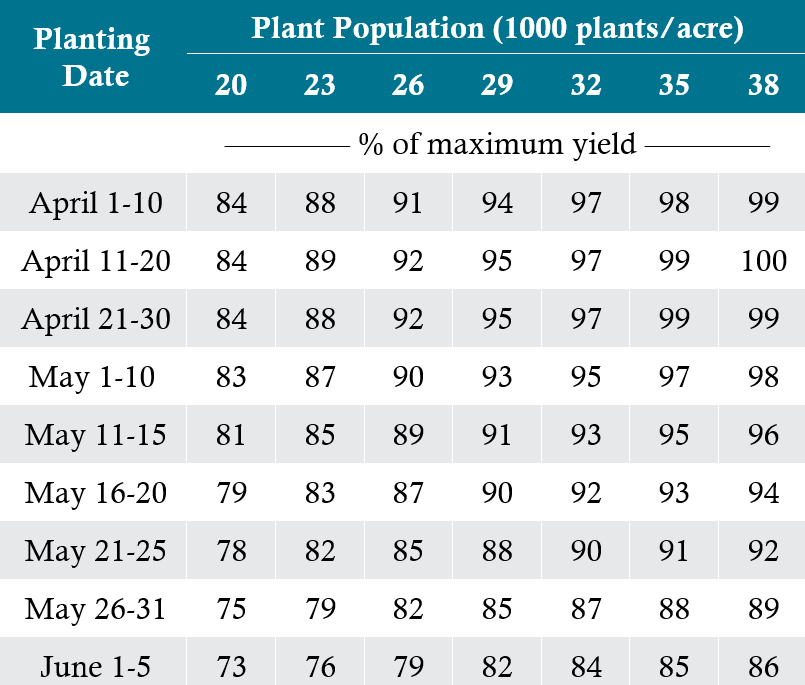
Source: Nafziger, E. 2020. Replanting Corn and Soybeans. farmdoc daily (10):89, Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, May 14, 2020.